Induction: July 2015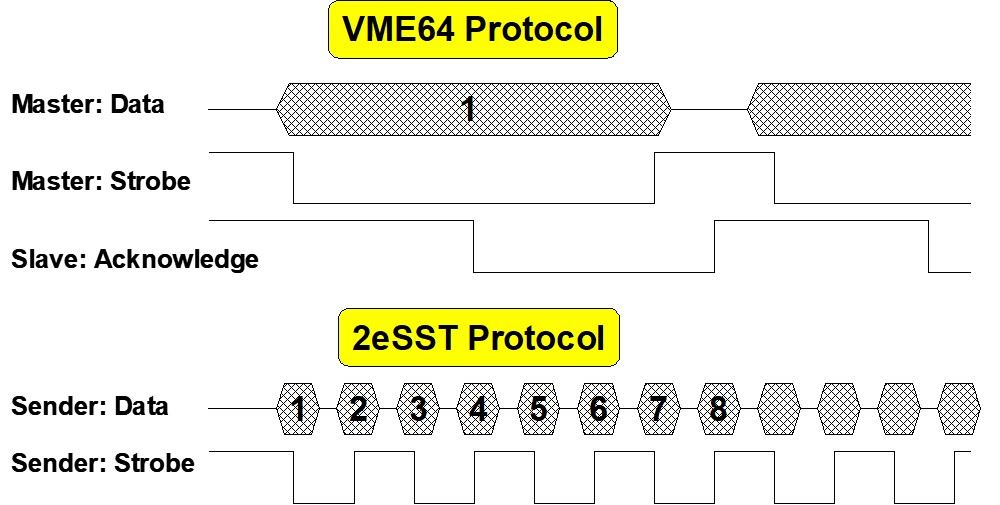
VMEbus started on its path to significant performance improvements while still remaining backwards compatible with legacy systems with the introduction of the VME64 concept. In 1989, John Peters of Performance Technologies developed the initial concept of VME64: multiplexing address and data lines (A64/D64) on the VMEbus. The concept was demonstrated the same year and submitted to the VITA Technical Committee in 1990 as a performance enhancement to the VMEbus specification.
Key Contributions
- 1989: John Peters and Bill Mahussen (Performance Technologies) developed the use of 64-bit multiplexed block transfer (MBLT) cycles and presented the VME64 concept to the VITA Technical Committee.
- 1990: Newbridge Microsystems released DARF 64 VME64 silicon.
- 1990: Performance Technology won the BUSCON Product of the Year award for VME64.
- 1991: VME64 (1014 Rev. D) was introduced and submitted to IEEE, raising the theoretical bus speed from 40 MBps to 80 MBps. The IEEE granted project authorization request (PAR) for P1014R (revisions to the VMEbus specification). Kim co-chaired the activity with Ray Alderman, technical director of VITA.
- 1992: Additional enhancements proposed to the VME64 specification were placed in VITA subcommittee: the VME64 Extensions Document. Two other activities began in late 1992: (1) VMEbus Board-Level Live Insertion specifications (BLLI), and (2) VMEbus System-Level Live Insertion with fault tolerance (VSLI).
- 1992: Newbridge Microsystems marketed the SCV64 single-chip VME64 interface.
- 1993: VITA subcommittees completed VME64.
- 1994: VERO Electronics offered a VME64 backplane.
- 1994: VME64 (ANSI/VITA 1) became the first VITA specification to receive ANSI approval. It defines the main body of the VMEbus specification and includes both 32- and 64-bit usage models.
- 1996: IP I/O Mapping to VME64x (ANSI/VITA 4.1) was approved, defining the pin assignments from IP modules to the VME64x P0 and P2 connectors.
- 1997: VME64 Extensions (ANSI/VITA 1.1) was approved as an extension to the VME64 specification, including the 160-pin connector, geographical addressing, and added power pins.
- 1997: VME64x 9U x 400 mm Format (ANSI/VITA 1.3) – Defines a 9U x 400 mm board layout for use within the VMEbus framework.
- 1998: VMEbus International Physics Association (VIPA, which includes CERN, Fermilab, and labs in Japan) rolled out VME64 Extensions for Physics (ANSI/VITA 23), which defines a series of recommended practices for the use of VMEbus in the physics community.
- 2000: Keying for Conduction-Cooled VME64x (ANSI/VITA 1.6) was approved for VMEbus technology.
- 2003: Gigabit Ethernet on VME64x Backplanes (ANSI/VITA 31.1) – Defines a pin assignment and interconnection methodology for implementing a 10/100/1000BASE-T Ethernet switched network on a VME64x backplane.
